Some examples of the figures encluded in the text
From booklet 2 The Specific Way of Thinking of a Physicist
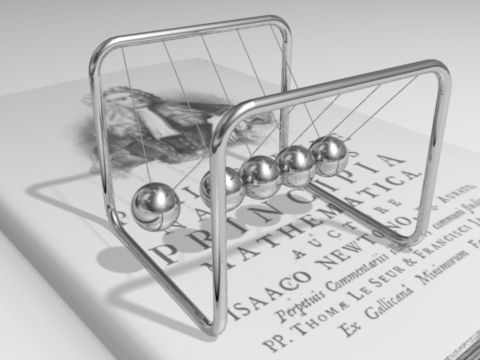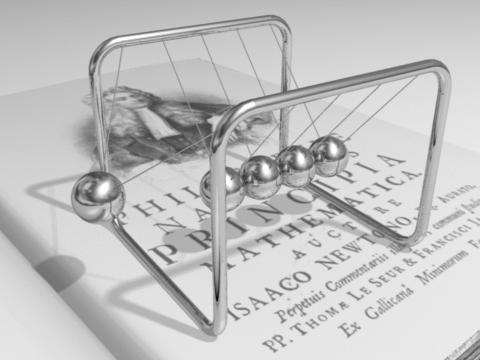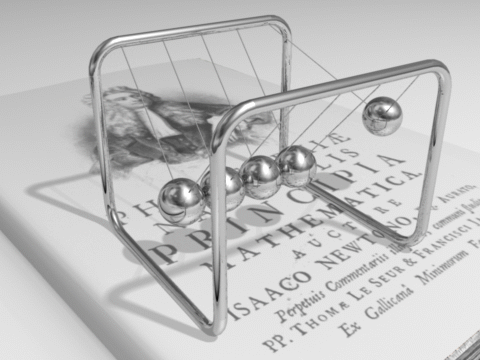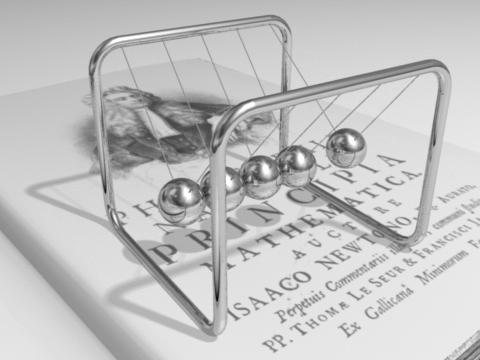
from Chapter 2.4 Balances and Conservation Laws :
Line pendulum of N balls fixed at a distance equal to the diameter of the balls
Example of a physical question which can be answered by just taking into account the conservation laws of energie and momentum
From booklet 3 Mechanics:

From paragraph 3.1.3 The Basics of Modern Mathematics
Demonstration of the topological aequivalence of a mug and a torus
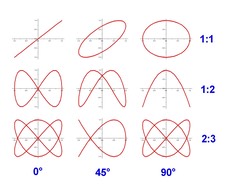
Lissajous figures with an amplitude-ratio of 1:1,a frequency ratio of 1:1 / 1:2 / 2:3 and a phase difference of 0 / 45° / 90°
(origin: designed by the autor)

Solar eclipse on the Cassini space probe at the 15.09.2006
(colour contrast enhanced original image)
(origin: http://jpl.nasa.gov/figures/PIA08329\_fig2.jpg)
From booklet 8 Thermodynamics:
from paragraph 8.1.18 The Energy Type Surface Energy
Structure of an oil-in-water emulsion (suncream) - image size 40 µm / 10 µm
(source: confocal microscope image taken by the author)

City Hall of Taos (New Mexico/USA) as an example of a modern building
in the Pueblo construction methode
(source: photo taken by the author)

from paragraph 8.8.3 Global thermal equalising currents / the global climate
A danish perspective: view of northern europe
taken from the International Space Station ISS (26.02.2003)
(source: NASA image gallery)
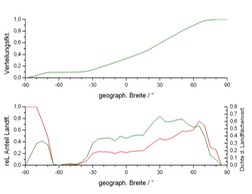
from paragraph 8.8.4 Global Climat Change:
Actual altitude-distribution of landscape
(a) distribution function of the normaliesed landscape
(b) over the altitude averaged relative fraction of landscape (red) and altitude-related density of landscape (green)
(source: graphic designed by the author)
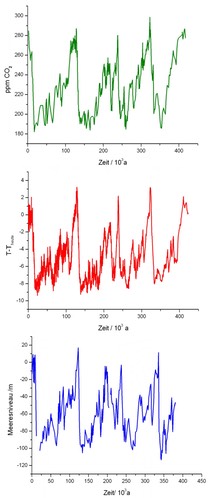
from paragraph 8.8.5 A Hypothesis explaining the Global Climate:
Chronological sequence of
CO2-concentration of the earth atmosphere (green),
ground temperature (red) and
see level (blue) during the pleistocene
(source: graphic designed by the author based on data published via
ftp://ftp.ncdc.noaa.gov/pub/data/paleo/contributions\_by\_author/siddal2003 and
http://www.cru.uea.ac.uk/cru/data/temperature)
from book 10 Elementary Particles, Cosmology:

Image of the Andromeda galaxy
(a) in the visible light
(b) as superposition of a sub-mm-radiation image (orange)
and an x-ray image (blue)
(Source: This image is based on the image
M31-andromeda_H of the ESA Multimedia Galery)
From booklet 11 Optik:
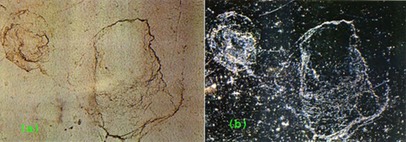
from paragraph 11.10.4 Contrast generating Effects
of Imaging Optical Instruments:
Image of a water patch on a painted car
(a) under bright field illumination
(b) under dark field illumination
(source: images taken by the author)
From booklet 12 Materials Science:

from paragraph 12.1.3 Why are construction concepts size dependent?
Skeleton of a Tyranno saurian exposed in the Royal Museum of Paleontology
in Drumheller/Alberta (Kanada)
(source: photo taken by the author)
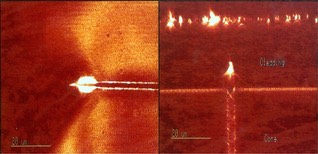
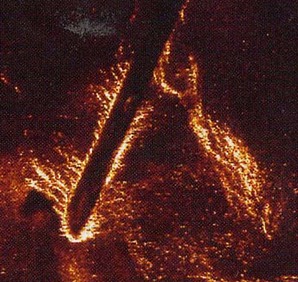
from paragraph 12.3.4 Non-linearity and geometrie dependancy:
Plastical Zone near the crack tip
CLSM-image of a Polycarbonate optical fibre
(source: confocal microscopic image taken by the author)
from paragraph 12.7.4 The Filler/Matrix-Interface:
CLSM-image of a short fibre reinforced polybutadiene/polyamide blend
after long-term alternating mechanical load
(source: confocal microscopic image taken by the author)


from paragraph 12.9.3 Anisotropic Composites:
Tappan Zee Bridge over the Hudson River
(nearby Tarrytown/New York State/USA)
Photo showing some details of the steel construction
(source: photo taken in 1994 by the author)
from paragraph 12.9.3 Anisotropic composites
Experiment showing the tensile strength of Polystal
mass of the Mini-truck = 4 t ; Polystal-diameter = 7,5 mm
(source: Research-Bayer-Forschungsmagazin, 1986, S. 34-41)
from book 14 Electronics:
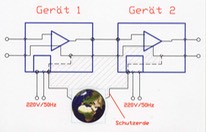
from paragraph 14.7.2 Techniques reducing parasite signals
Typical structure of the electrical connections between 2 electronic devices